
WORMHOLES:COSMIC SHORTCUTS
What if you could rocket from Earth, not to the Moon or Mars, but down a wormhole that loops all the way across the vast Milky Way, slashing travel time
The Artemis is currently an exciting project by NASA that seeks to place humans on the lunar surface for the second time but sustainably. It was thus christened Artemis after the Greek goddess of the moon and the twin sister of Apollo, the project is expected to redefine human capacities and technological advancement, and global collaboration.
The first and foremost of the Artemis program goals is to send ‘the first woman and the next man’ to the lunar south pole in 2024. Nonetheless, Artemis goes beyond the single mission as one of the plans of exploration by the human being. The program seeks to:
Sustain Human Presence: As the last step, set up the permanent human presence on the surface of the Moon by the end of the decade. This implies establishing the facilities that would enable the creation of a sustainable lunar living and research environment.
Advance Lunar Science: Establish a scientific laboratory that is beyond our Earthly one that involves research on the Moon to discover more about the solar systems and the universe.
Test Technologies for Mars: Be used to test sorts of technologies and procedures that will be employed in the subsequent missions on Mars. This entails the issuance of life support systems, construction of habitats, and resource use.
Economic and International Collaboration: Treat outer space as the common frontier for cooperation and use the Lunar initiatives as an impetus to stimulate new industries and ‘‘grow the pie’’ of the world economy.
The Technology Behind Artemis
Technologies and systems supporting the Artemis program have been developed with specific response to the problems faced when conducting research on the surface of the moon as well as to guarantee the efficiency of the missions.
Space Launch System (SLS): As is well known the SLS is the most powerful rocket that NASA has been able to develop so far. Its intended task is to transport astronauts on the Orion spacecraft to the Moon. Capable of producing 8.8 million pounds of thrust, this SLS will be the key of Artemis missions and the primary of lunar landing.
Orion Spacecraft: Orion is a new spaceship that the National aeronautics and space administration of the United States uses for traveling in deep space. It is intended to transport astronauts to the Moon and back with protection, control, oxygen, and heat/shield systems.
Lunar Gateway: Lunar Gateway is basically a space station that is set to orbit around the moon and function as a sort of hub with some specific missions to the actual lunar surface. It will supplement the long-term lunar presence and wants to become an international space station for regional and commercial collaborators.
Human Landing System (HLS): HLS will be the system that will transport the astronauts from the space station or what is known as the Lunar Gateway to the lunar surface. There are multiple commercial actors who are now building different versions of the HLS creating innovation and competition to lunar landings.
Lunar Surface Innovation Initiative: This also entails evolving the capabilities for lunar operations including robotics, automation and power capability and management.
Consequences of long term presence on moon
Developing a long-term habitation on the Moon will alter the world in terms of scientific advancements, technologies, and mankind’s prospect for exploring the cosmos.
Scientific Discovery: The Moon presents scientists with a rather specific context when it comes to carrying out their tasks and investigations. The surface of this moon contains fossils of the early solar system and the permanently frozen areas may have water ice, which is critical for research as well as having practical uses for astronauts.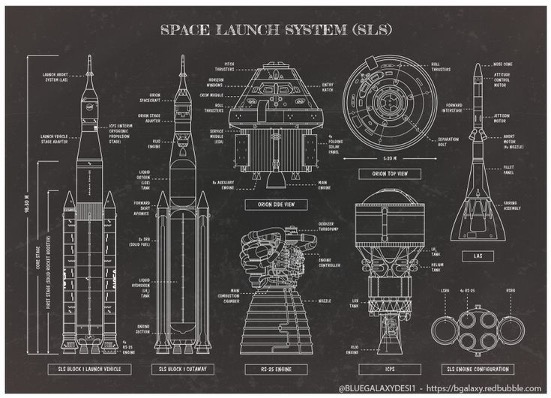
Technological Advancement: The environment probably will force humans to invent new tools and techniques of existence and survival on the Moon. These will go beyond astrophysics as they have impact on industries on earth, ranging from material science to renewable energy.
Pathway to Mars: Such a sustainable lunar exploration prepares for the subsequent missions to Mars due to the gained experience. Lunar missions help in developing the technologies and plans that will be necessary in further space exploration such as using structures, resources, and oxygen.
International and Commercial Collaboration: Artemis is not just a scale at NASA; it is somewhere that is for all societies of the globe. This way, Artemis combines global collaboration and new economic sectors based on international space agencies and companies.
Inspiration and Education: Again, the return to the Moon will ignite the interest of young scientists, engineers, and explorers. That is why the mentioned program’s focus on diversity and inclusion, for instance, the target to send the first woman to the lunar surface, can be seen as the program’s ability to inspire people of diverse backgrounds to explore the unknown space frontiers.
Conclusion
The Artemis program is one of the greatest leaps in the exploration of space by human beings. Through lunar missions and creating long-term lunar presence, NASA and its industrial collaborators are preparing for the further conquest of the solar system. Everything that starts with Artemis – technological advances, new scientific discoveries, and cooperation with other countries – will help not only explore the universe but also improve life on the planet. Thus, as we are on the verge of this new epoch in human history, the Moon emerges as a focus of people’s curiosity, desire, and creativity.

What if you could rocket from Earth, not to the Moon or Mars, but down a wormhole that loops all the way across the vast Milky Way, slashing travel time

If you go outdoors on a clear evening and also search for it, you might have the ability to see Jupiter beaming brilliantly amongst the celebrities. At the exact same

Stars, the dazzling points of light that fill up the evening skies are the foundation of galaxies plus the cradles of life itself. From their birth in large clouds of

In the mission to recognize deep space mankind has actually developed progressively effective devices to observe deep space. Completion of this venture is the Extremely Large Telescope (ELT) which is

Space debris, also known as space junk, refers to the defunct artificial objects orbiting Earth. These objects include decommissioned satellites, spent rocket stages, and fragments from collisions and explosions.

The search for exoplanets– planets that orbit stars outside our planetary system– has actually quickly developed into one of the most interesting and dynamic fields of astronomy
Write to
Jasmine Gogoi at csr@scientifictemperament.com
Let’s develop our society with a scientific heart. Join us to build the scientifically nurtured future →